Experiment paradigm
Due to relevent article under double blind review, contents are not fully updated here, will be uodated soon..
Ethical Approval
Ethical Approval: The ethical approval for conducting experiment with human, was taken from Queen Mary Ethics of Research Committee, of Queen Mary University of London. All the participants also signed a consent form to record and use the data for research purpose.
Experiment Design
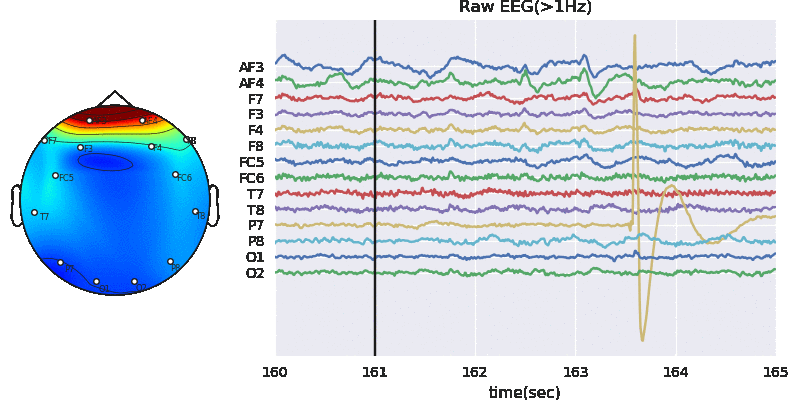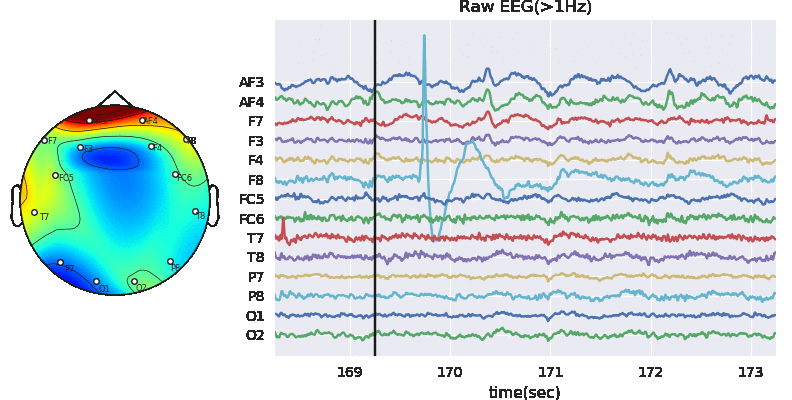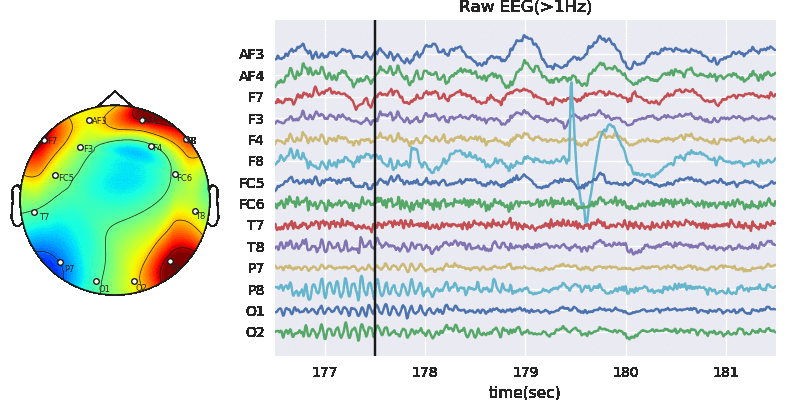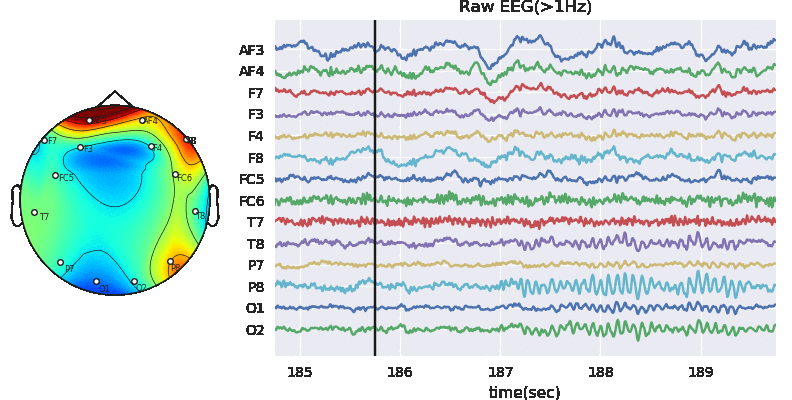
The experiment is based on listening task, unlike diachotic listening task, each subject was presented only one auditory stimulus under different auditory conditions for 1 trial. As shown in Figure 1. The auditory conditions include different level of background noise (N), Sementicity (S) and length (L) of audio stimulus. Each subject was presented with 144 stimuli, one per trial, with no repeatition of audio message. The order of stimuli with different auditory conditions were randomized. The physiological signals (R) were recorded at sampling rate of 128 Hz.
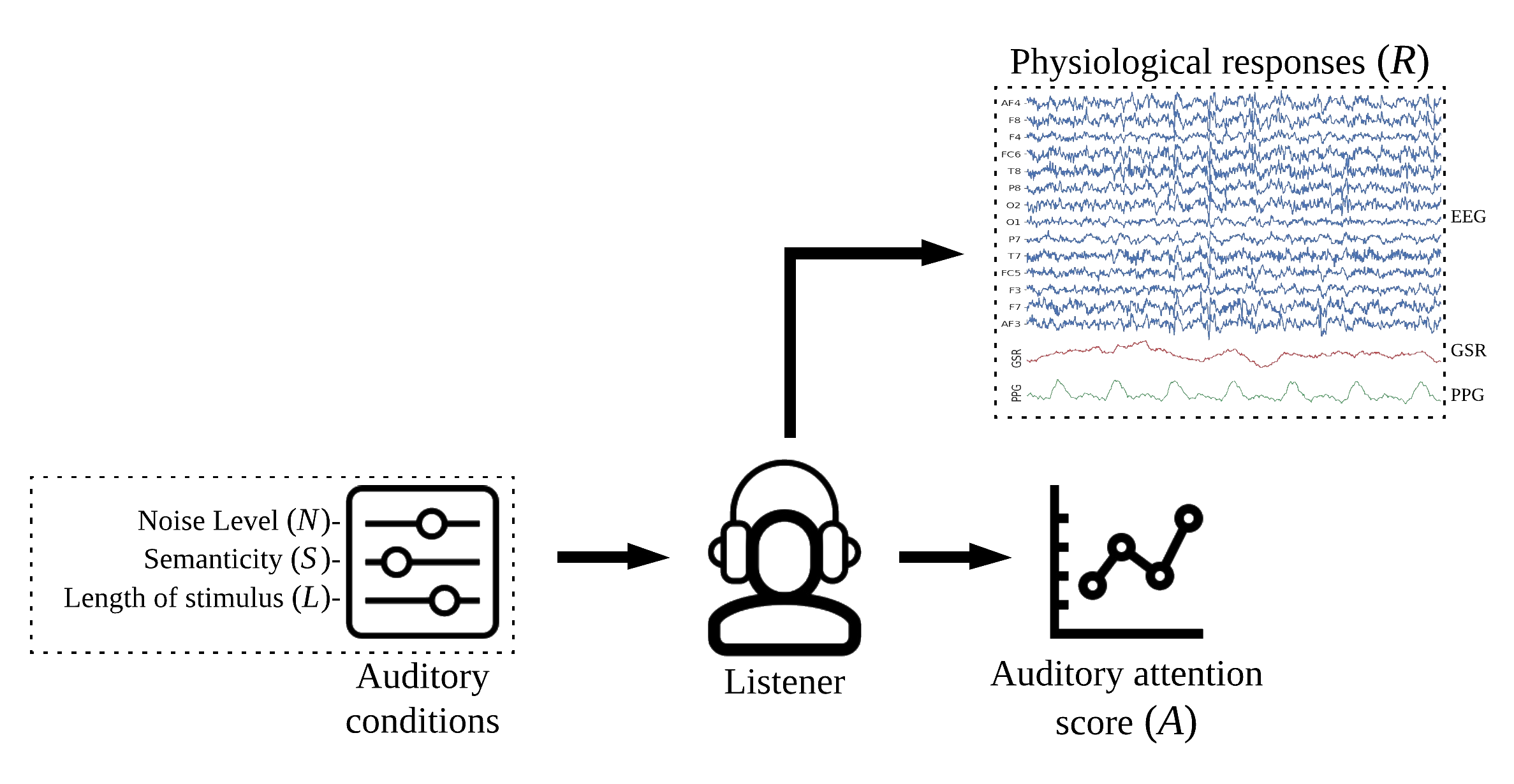
For computing the “Auditory Attention Score (A)”, following the literature, the number of correctly identetified words \(N_C\)) in the trasncriped audio message were counted and Attention Score \(A = \frac{N_C}{N_T}\times 100\), computed where \(N_T\) is total words in the original audio message.
Experimental procedure
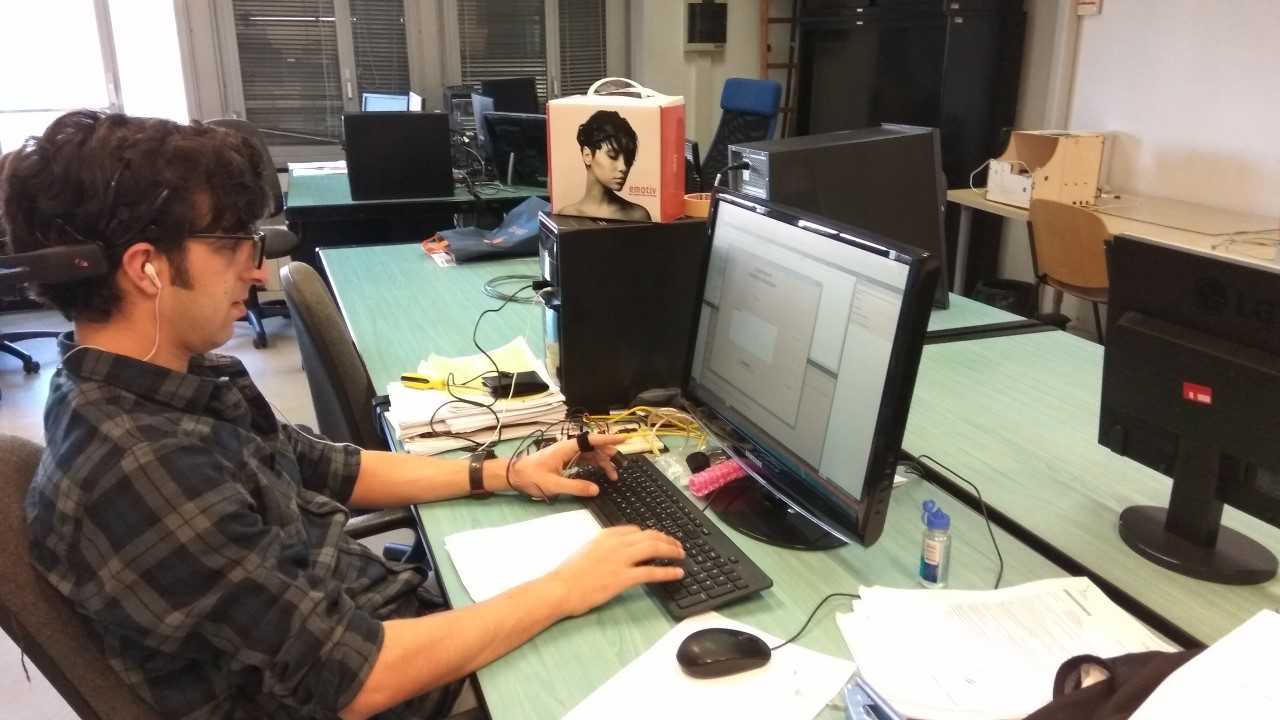
As shown in Figure 2 below (in right), each trial consists of three tasks, listerning, writing, and resting. Using a computer interfact, A subject can actively choose to play an audio stimulus while listerning task. Once audio is finished, subject needs to transcribe the message (writing task). Audio can not be reproduced (replayed). Once transcription is done, writing task can be finished by submit button. The duration between writing task and next listening task is labeled as resting task. On the average total time taken by one subject was \(40\pm10\). The pitcute of a participent performing the experiment is shown below (on the left side).


Predictive tasks
Following four preditive tasks are formulated. The details of formulation and respective justification is explained in the paper.
\[\begin{eqnarray} \text{T1: Attention Score prediction} &:& A^{\prime} = f_A(F_r)\\ \text{T2: Noise Level prediction} &:& N^{\prime} = f_N(F_r)\\ \text{T3: Semanticity prediction} &:& S^{\prime} = f_S(F_r)\\ \text{T4: LWR Classification} &:& \mathcal{T}^{\prime} = f_{\mathcal{T}}(F_r) \end{eqnarray}\]where \(F_r\) is feature vector extracted from Physiological Responses \(R\): \(R \rightarrow F_r\)
Participents - demographics
A total of 25 participants, 21 Males, 4 Females, from 10 different nationalities with 11 different first languages, majority age group of 26-30 were chosen for the experiment.
| Nationality | #Participants | First language | #Participants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algerian | 1 | Arabic | 7 | |
| Indian | 8 | Farsi | 3 | |
| Iranian | 3 | Italian | 4 | |
| Italian | 4 | Kannada | 1 | |
| Kazakh | 1 | Kazakh | 1 | |
| Lebanese | 4 | Mathili | 1 | |
| Moroccan | 1 | Malayalam | 4 | |
| Nepalese | 1 | Marathi | 1 | |
| Pakistani | 1 | Tamil | 1 | |
| Tunisian | 1 | Telgu | 1 | |
| Urdu | 1 |
| Sex | #Participants | Age Group | #Participants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 21 | 16-20* | 1 | |
| Female | 4 | 21-25 | 6 | |
| 26-30 | 16 | |||
| 31-35 | 2 |
*Age of >=18, no parents conset was required
Collected Dataset
For details about collected dataset - please see here